
leads4pass 312-50v12 dumps contain 528 latest exam questions and answers for the 2023 CEH v12 certification exam. Practice the latest 312-50v12 certification exam questions using PDF and VCE lightweight tools with accurate answers and explanations of difficult questions to ensure 100% success in passing the CEH v12 certification exam.
Welcome to download 312-50v12 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/312-50v12.html, to ensure success as a member of the World’s Number 1 Ethical Hacking.
Read the latest 312-50v12 dumps exam questions online:
| Number of exam questions | Exam name | Exam code | Last updated |
| 15 | Certified Ethical Hacker Exam | 312-50v12 | 312-50v11 dumps |
QUESTION 1:
When configuring wireless on his home router, Javik disables SSID broadcast. He leaves authentication “open” but sets the SSID to a 32-character string of random letters and numbers.
What is an accurate assessment of this scenario from a security perspective?
A. Since the SSID is required in order to connect, the 32-character string is sufficient to prevent brute-force attacks.
B. Disabling SSID broadcast prevents 802.11 beacons from being transmitted from the access point, resulting in a valid setup leveraging “security through obscurity”.
C. It is still possible for a hacker to connect to the network after sniffing the SSID from a successful wireless association.
D. Javik’s router is still vulnerable to wireless hacking attempts because the SSID broadcast setting can be enabled using a specially crafted packet sent to the hardware address of the access point.
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 2:
An attacker identified that a user and an access point are both compatible with WPA2 and WPA3 encryption.
The attacker installed a rogue access point with only WPA2 compatibility in the vicinity and forced the victim to go through the WPA2 four-way handshake to get connected.
After the connection was established, the attacker used automated tools to crack WPA2-encrypted messages.
What is the attack performed in the above scenario?
A. Timing-based attack
B. Side-channel attack
C. Downgrade security attack
D. Cache-based attack
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 3:
John, a disgruntled ex-employee of an organization, contacted a professional hacker to exploit the organization.
In the attack process, the professional hacker Installed a scanner on a machine belonging to one of the victims and scanned several machines on the same network to Identify vulnerabilities to perform further exploitation.
What is the type of vulnerability assessment tool employed by John in the above scenario?
A. Proxy scanner
B. Agent-based scanner
C. Network-based scanner
D. Cluster scanner
Correct Answer: C
Explanation
Explanation/Reference:
Network-based scanner
A network-based vulnerability scanner, in simplistic terms, is the process of identifying loopholes in a computer’s network or IT assets, which hackers and threat actors can exploit.
By implementing this process, one can successfully identify their organization’s current risk(s).
This is not where the buck stops; one can also verify the effectiveness of your system’s security measures while improving internal and external defenses.
Through this review, an organization is well equipped to take an extensive inventory of all systems, including operating systems, installed software, security patches, hardware, firewalls, anti-virus software, and much more.
Agent-based scanner
Agent-based scanners make use of software scanners on each and every device; the results of the scans are reported back to the central server. Such scanners are well-equipped to find and report on a range of vulnerabilities.
NOTE:
This option is not suitable for us, since for it to work, you need to install a special agent on each computer before you start collecting data from them.
QUESTION 4:
There have been concerns in your network that the wireless network component is not sufficiently secure.
You perform a vulnerability scan of the wireless network and find that it is using an old encryption protocol that was designed to mimic wired encryption, what encryption protocol is being used?
A. WEP
B. RADIUS
C. WPA
D. WPA3
Correct Answer: A
Explanation
Explanation/Reference:
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) may be a security protocol, laid out in the IEEE wireless local area network (Wi-Fi) standard, 802.11b, that’s designed to supply a wireless local area network (WLAN) with A level of security and privacy like what’s usually expected of a wired LAN.
A wired local area network (LAN) is usually protected by physical security mechanisms (controlled access to a building, for example) that are effective for a controlled physical environment but could also be ineffective for WLANs because radio waves aren’t necessarily bound by the walls containing the network.
WEP seeks to determine similar protection thereto offered by the wired network’s physical security measures by encrypting data transmitted over the WLAN. encoding protects the vulnerable wireless link between clients and access points; once this measure has been taken, other typical LAN security mechanisms like password protection, end-to-end encryption, virtual private networks (VPNs), and authentication are often put in situ to make sure privacy.
A research group from the University of California at Berkeley recently published a report citing “major security flaws” in WEP that left WLANs using the protocol susceptible to attacks (called wireless equivalent privacy attacks). within the course of the group’s examination of the technology, they were ready to intercept and modify transmissions and gain access to restricted networks.
The Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA) claims that WEP ? which is included in many networking products. was never intended to be the only security mechanism for a WLAN, and that, in conjunction with traditional security practices, it’s very effective.
QUESTION 5:
Which type of malware spreads from one system to another or from one network to another and causes similar types of damage as viruses to do to the infected system?
A. Rootkit
B. Trojan
C. Worm
D. Adware
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 6:
How does a denial-of-service attack work?
A. A hacker prevents a legitimate user (or group of users) from accessing a service
B. A hacker uses every character, word, or letter he or she can think of to defeat authentication
C. A hacker tries to decipher a password by using a system, which subsequently crashes the network
D. A hacker attempts to imitate a legitimate user by confusing a computer or even another person
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 7:
When you are getting information about a web server, it is very important to know the HTTP Methods (GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, DELETE, TRACE) that are available because there are two critical methods (PUT and DELETE). PUT can upload a file to the server and DELETE can delete a file from the server.
You can detect all these methods (GET, POST, HEAD, DELETE, PUT, TRACE) using the NMAP script engine.
What Nmap script will help you with this task?
A. HTTP-methods
B. HTTP enum
C. HTTP-headers
D. HTTP-git
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 8:
What is not a PCI compliance recommendation?
A. Use a firewall between the public network and the payment card data.
B. Use encryption to protect all transmission of cardholder data over any public network.
C. Rotate employees handling credit card transactions on a yearly basis to different departments.
D. Limit access to cardholder data to as few individuals as possible.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation
Explanation/Reference:
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/pci_security/maintaining_payment_security Build and Maintain a Secure Network
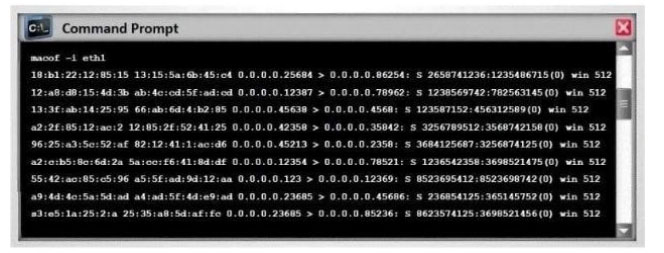
In a MAC flooding attack, a switch is fed with many Ethernet frames, each containing different source MAC addresses, by the attacker. Switches have limited memory for mapping various MAC addresses to physical ports.
What happens when the CAM table becomes full?
A. Switch then acts as a hub by broadcasting packets to all machines on the network
B. The CAM overflow table will cause the switch to crash causing Denial of Service
C. The switch replaces the outgoing frame switch factory default MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF: FF
D. Every packet is dropped and the switch sends out SNMP alerts to the IDS port
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 10:
Insecure direct object reference is a type of vulnerability where the application does not verify if the user is authorized to access the internal object via its name or key.
Suppose a malicious user Rob tries to get access to the account of a benign user Ned.
Which of the following requests best illustrates an attempt to exploit an insecure direct object reference vulnerability?
A. “GET /restricted/goldtransfer?to=Rob&from=1 or 1=1′ HTTP/1.1Host: westbank.com”
B. “GET /restricted/\r\n\%00account%00Ned%00access HTTP/1.1 Host: westbank.com”
C. “GET /restricted/accounts/?name=Ned HTTP/1.1 Host westbank.com”
D. “GET /restricted/ HTTP/1.1 Host: westbank.com
Correct Answer: C
Explanation
Explanation/Reference:
This question shows a classic example of an IDOR vulnerability. Rob substitutes Ned’s name in the “name” parameter and if the developer has not fixed this vulnerability, then Rob will gain access to Ned’s account.
Below you will find more detailed information about IDOR vulnerability.
Insecure direct object references (IDOR) are a cybersecurity issue that occurs when a web application developer uses an identifier for direct access to an internal implementation object but provides no additional access control and/or authorization checks.
For example, an IDOR vulnerability would happen if the URL of a transaction could be changed through client-side user input to show unauthorized data of another transaction. Most web applications use simple IDs to reference objects.
For example, a user in a database will usually be referred to via the user ID. The same user ID is the primary key to the database column containing user information and is generated automatically. The database key generation algorithm is very simple: it usually uses the next available integer.
The same database ID generation mechanisms are used for all other types of database records.
The approach described above is legitimate but not recommended because it could enable the attacker to enumerate all users. If it’s necessary to maintain this approach, the developer must at least make absolutely sure that more than just a reference is needed to access resources.
For example, let’s say that the web application displays transaction details using the following URL:
https://www.example.com/transaction.php?id=74656
A malicious hacker could try to substitute the id parameter value 74656 with other similar values, for example:
https://www.example.com/transaction.php?id=74657
The 74657 transactions could be valid transactions belonging to another user. The malicious hacker should not be authorized to see it. However, if the developer made an error, the attacker would see this transaction, and hence we would have an insecure direct object reference vulnerability.
QUESTION 11:
Session splicing is an IDS evasion technique in which an attacker delivers data in multiple, small-sized packets to the target computer, making it very difficult for an IDS to detect the attack signatures.
Which tool can be used to perform session splicing attacks?
A. TCP splice
B. Burp
C. Hydra
D. Whisker
Correct Answer: D
Explanation
Explanation/Reference:
Many IDS reassemble communication streams; hence, if a packet is not received within a reasonable period, many IDS stop reassembling and handling that stream. If the application under attack keeps a session active for a longer time than that spent by the IDS on reassembling it, the IDS will stop.
As a result, any session after the IDS stops reassembling the sessions will be susceptible to malicious data theft by attackers. The IDS will not log any attack attempt after a successful splicing attack. Attackers can use tools such as Nessus for session splicing attacks.?
Did you know that the EC-Council exam shows how well you know their official book? So, there is no “Whisker” in it. In the chapter “Evading IDS” -> “Session Splicing”, the recommended tool for performing a session-splicing attack is Nessus.
Where Wisker came from is not entirely clear, but I will assume the author of the question found it while copying Wikipedia.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intrusion_detection_system_evasion_techniques One basic technique is to split the attack payload into multiple small packets so that the IDS must reassemble the packet stream to detect the attack.
A simple way of splitting packets is by fragmenting them, but an adversary can also simply craft packets with small payloads. The ‘whisker’ evasion tool calls crafting packets with small payloads ‘session splicing’.
By itself, small packets will not evade any IDS that reassembles packet streams. However, small packets can be further modified in order to complicate reassembly and detection. One evasion technique is to pause between sending parts of the attack, hoping that the IDS will time out before the target computer does. A second evasion technique is to send the packets out of order, confusing simple packet re-assemblers but not the target computer.
NOTE: Yes, I found scraps of information about the tool that existed in 2012, but I can not give you unverified information. According to the official tutorials, the correct answer is Nessus, but if you know anything about Wisker, please write in the QA section. Maybe this question will be updated soon, but I’m not sure about that.
QUESTION 12:
Which Intrusion Detection System is the best applicable for large environments where critical assets on the network need extra scrutiny and is ideal for observing sensitive network segments?
A. Honeypots
B. Firewalls
C. Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS)
D. Host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 13:
Given below are the different steps involved in the vulnerability-management life cycle.
1) Remediation
2) Identify assets and create a baseline
3) Verification
4) Monitor
5) Vulnerability scan
6) Risk assessment
Identify the correct sequence of steps involved in vulnerability management.
A. 2–>5–>6–>1–>3–>4
B. 2–>1–>5–>6–>4–>3
C. 2–>4–>5–>3–>6–> 1
D. 1–>2–>3–>4–>5–>6
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 14:
Miley, a professional hacker, decided to attack a target organization’s network. To perform the attack, she used a tool to send fake ARP messages over the target network to link her MAC address with the target system’s IP address.
By performing this, Miley received messages directed to the victim’s MAC address and further used the tool to intercept, steal, modify, and block sensitive communication to the target system.
What is the tool employed by Miley to perform the above attack?
A. Gobbler
B. KDerpNSpoof
C. BetterCAP
D. Wireshark
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 15:
ViruXine.W32 virus hides its presence by changing the underlying executable code.
This Virus code mutates while keeping the original algorithm intact, the code changes itself each time it runs, but the function of the code (its semantics) will not change at all.
Here is a section of the Virus code:

What is this technique called?
A. Polymorphic Virus
B. Metamorphic Virus
C. Dravidic Virus
D. Stealth Virus
Correct Answer: A
…
528 latest exam questions and answers are verified by a professional team. They are authentic and effective. Download leads4pass 312-50v12 dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/312-50v12.html to ensure successful passing of the Certified Ethical Hacker CEHv12 certification exam.




